Tech
Big Data Specialist Kills

A big data analyst is a versatile specialist who has knowledge in mathematics, statistics, information science, computer science, business and economics. A Big Data analyst studies large amounts of data containing disparate information, for example, research results, market trends, customer preferences, etc. Research and analysis of such information can lead to new scientific discoveries, increased company performance, new income opportunities, improved customer service etc. The main skill of scientists is to see logical connections in the system of collected information and, on the basis of this, develop certain business solutions and models.
Big Data analysts need to be able to extract the information they need from all sorts of sources, including information flows in real time, and analyze it for further business decision making. It is not only a matter of the amount of information processed, but also of its heterogeneity and speed of updating.
Today, the term is usually used to refer not only to the datasets themselves, but also the tools for processing them and the potential benefits that can be obtained as a result of painstaking analysis. The main characteristics that distinguish Big Data from another kind are three Vs: volume (large volumes), velocity (the need for fast processing), and variety. Hire big data programmer to know more.
There are two main specializations for people who want to work with big data:
- Big Data engineers are more responsible for storing, transforming data and fast access to it;
- Big Data analysts are responsible for analyzing big data, identifying relationships and building models.
The main demand for analysts is formed by IT and telecom companies and large retail chains. Recently, it has been increasingly used in the banking sector, public administration, and agriculture. Engaging a specialist is an opportunity to look at the available data from different angles.
What you need to know and be able to
Personal qualities:
- Fast learner;
- Critical thinking;
- Analytical mind;
- Attention to details;
- A responsibility;
- Broad outlook;
- Ability to follow through on research despite unsuccessful interim results;
- Ability to explain complex things in simple words;
- Business intuition.
Basic skills
- Thorough knowledge of the industry in which the work takes place;
- Possession of statistical tools SPSS, R, MATLAB, SAS Miner, Tableau;
- Deep knowledge of methods of statistical analysis, construction of mathematical models (neural networks, Bayesian networks, clustering, regression, factorial, variance and correlation analyzes, etc.);
- ETL (Extraction, Transformation, Loading) – extracting from various sources, transforming it for analysis, loading it into an analytical database;
- Ability to set a task for database specialists;
- Fluency in SQL;
- Knowledge of English at the level of reading technical documentation;
- Knowledge of scripting programming languages Python / Ruby / Perl;
- Machine learning skill;
- Ability to work in Hadoop, Google big table.
Responsibilities
Any analyst deals with scattered information that needs to be structured correctly, namely, to conduct:
- building a data collection process for the possibility of their subsequent operational processing;
- ensuring the completeness and interconnection from different sources;
- development of solutions to optimize current processes based on the results of the analysis.
Business
How Good is Skrill in Protecting Your Data in iGaming?

Skrill is considered one of many payment methods for iGaming. The question that may arise is: how good is it in terms of data protection? This guide will discuss this in more detail. Understandably, people have valid concerns about their data security.
For its part, many iGaming platforms hold it to a high level of importance. This not only applies to their financial transactions but also to the data tied to their identity. Let’s continue through and discuss how Skrill could be a good option for iGaming when it comes to data.
So is Skrill really good when it comes to security?
The short answer is yes. A more detailed answer is that Skrill can maintain its reputation as one of the most secure digital wallets. It can be able to keep your bank details hidden while being able to stay one step ahead of any potential fraud. This will give you confidence and peace of mind using casinos with Skrill deposit.
In a setting like iGaming, you’ll be happy knowing that you have a payment method that offers excellent security. With platforms gaining in popularity, they want to be confident that their financial data is safe and sound.
What are the pros and cons of using Skrill in iGaming?
Skrill has its advantages and disadvantages in terms of iGaming platforms. It may have a strong case of being good for your personal needs and preferences. With this in mind, let’s take a look at the following pros first:
Pros
- Enhanced security: Of course, we’ve already stated this topic earlier on. If you are looking for what could be one of the most secure payment methods out there, look no further.
- Convenience: Skrill allows users to quickly deposit their funds into their gaming accounts. Thus, you can use it across several compatible platforms. It’s possible to get a seamless experience.
- Privacy: If you are looking for anonymity, you could get it at least in part. That’s because Skrill will keep your bank details private. No one will know your bank account number or anything else like that.
Cons
- Some fees may apply: Keep in mind that Skrill has to make its money one way or another. So some fees could apply. They may apply to transactions, currency conversion, and withdrawal fees.
- Verification process: While the stringent security measures can be a blessing, there may be one curse. But it’s a necessary evil for sure. Users of Skrill will need to undergo a verification process. This will allow them to use higher transactional limits and other additional features. It may lead to wait times that could be an inconvenience to users.
What are some tips for secure iGaming with Skrill?
Now that we have cleared up the pros and cons, we can provide some tips for secure iGaming. If you are using Skrill, it’s important to follow them accordingly. Let’s take a look at what they are:
Choose a reputable platform
It’s always a good idea to consider an iGaming platform that is reputable and highly rated. These sites will often take security seriously and protect user data. If it accepts Skrill, that’s even better.
Keep an eye on your transactions
Needless to say, monitoring your transactions regularly is a must. You’ll want to be on the lookout for any unauthorized charges or suspicious activity. While security tends to be tight, certain situations may arise where an unauthorized transaction may appear – like falling victim to a phishing attack.
Avoid potentially dangerous cyber attack attempts
Phishing emails are common – especially if they claim to be from reputable companies. Someone may claim to be from Skrill and ask for your information. It’s always a good idea to authenticate the communication by reaching out to customer service. Inquire about the email to see if what was sent was the real deal. You’ll get a straight answer from there.
Add additional security
This includes strong passwords and using 2FA features. These can play a huge role in keeping your Skrill account secure. And it can prevent unauthorized transactions from occurring.
If you are considering Skrill as a payment method, we hope this guide has helped. In addition, we hope it has given you the confidence to choose it as your go-to option. Choosing a secure payment method can help improve your overall iGaming experience. Especially when you want to keep things as secure as possible.
Features
Razer Gold for Less: Insider Tips for Buying Discounted Gift Cards on BuySellVouchers
Razer Gold is a virtual currency that is offered by the Razer company. You can use Razer Gold to purchase new games and in-game content. Usage Razer Gold gift cards give you a better bang for your buck and when you top up your Razer Gold, you get Razer Silver in return which you can exchange for even more rewards.
Every buyer loves a good discount no matter what product it is you’re buying. The same goes for buying discounted Razer Gold gift cards. Gamers tend to rely on gift cards a lot to make their gaming purchases. By using discounted gift cards, you can not only make your transaction almost instantly but also do it cost-effectively.
In this article, we’ll tell you all about buying discounted Razer Gold gift cards and how to utilize them in order to reap the maximum profits possible as well as addressing some common concerns and providing tips to make a smooth transaction.
Understanding Razer Gold and BuySellVouchers
Razer Gold is your all-in-one currency to purchase various games and in-game content from the Razer website. Razer Gold can be obtained by purchasing it directly or redeeming Razer Gold gift cards. Using Razer Gold vouchers is a much cheaper and convenient way to carry out all your gaming transactions.
Buying Razer Gold gift cards through BuySellVouchers
If you want to top up your Razer account, you can simply purchase a Razer Gold gift card. The smart choice would be to get a discounted Razer Gold gift card but where can a person get one? BuySellVouchers of course. BuySellVouchers has a huge category of discounted Razer Gold gift cards so you can browse and buy the one you deem best.
Discounted gift cards obviously save you money. So why not use them? By using discounted gift cards, you can purchase any game you want at a much cheaper price than buying it directly from official stores.
Why Choose BuySellVouchers for Razer Gold PINs?
Discounted Gift Cards
There are many reasons to choose BuySellVouchers for buying and selling gift cards over other platforms. One of the main reasons is discounts, which can reach up to 35% of the gift card’s nominal value. It has the best prices and special discounts across most of its products which makes BuySellVouchers a no-brainer if you want to purchase cheap gift cards. BuySellVouchers also has support for various payment methods including crypto such as USDT, BTC, USDC, and e-wallets like Maya and GrabPay (at the Official Store).
Razer Gold gift card giveaways
Every other week, BuySellVouchers provides gift card giveaways. Since users have the opportunity to select their preferred gift card platform for the giveaways, Razer Gold gift cards are frequently chosen. Each giveaway typically offers 10 gift cards, each valued at $10.
Comparison with other platforms offering Razer Gold gift cards
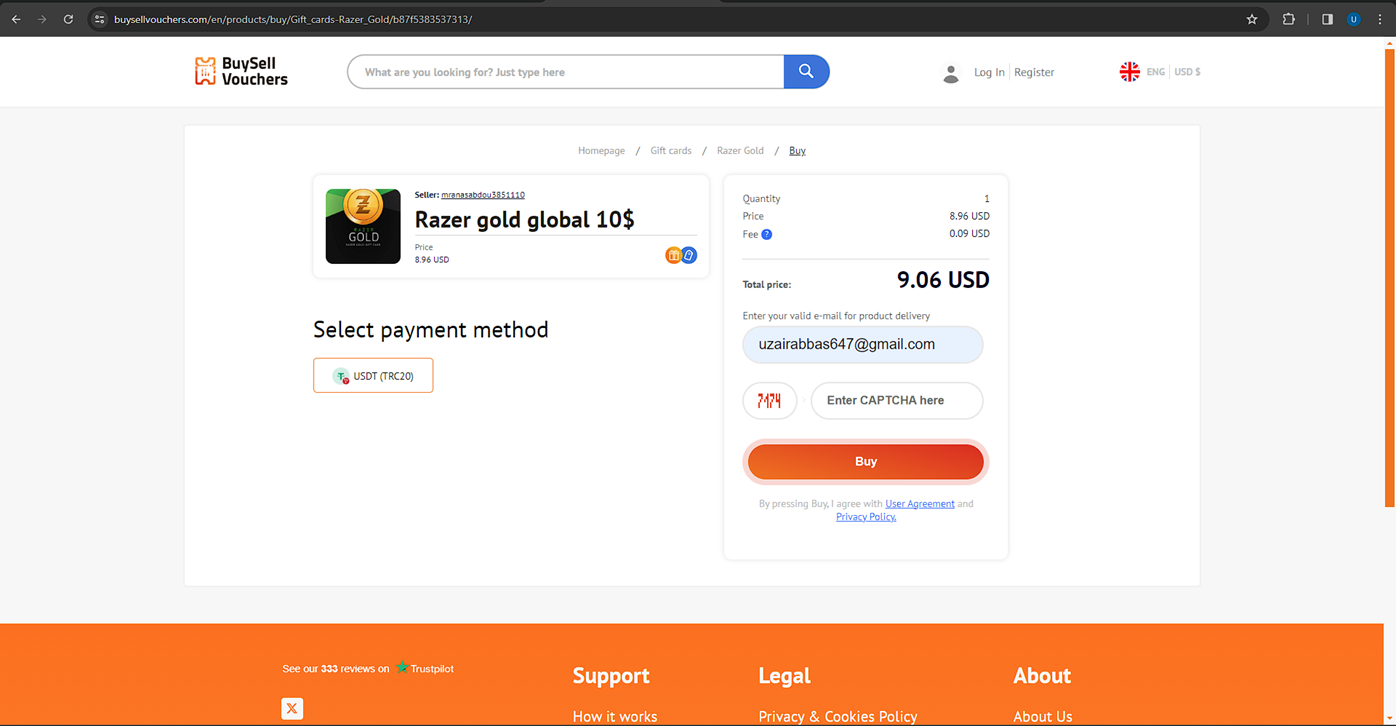
If we compare the price of the cheapest 10 USD Razer Gold gift card among some other popular marketplaces, we can see that BuySellVouchers offers the lowest price of 9.06 USD.
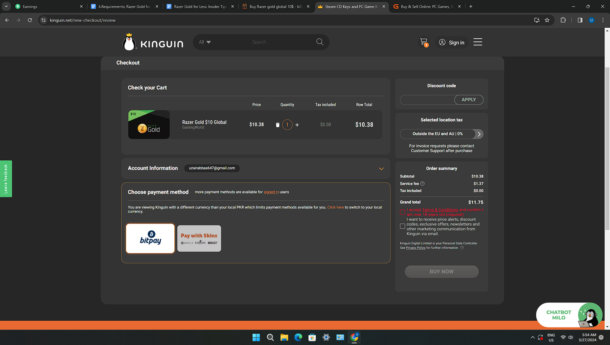
Kinguin.net has a price of 11.75 USD:
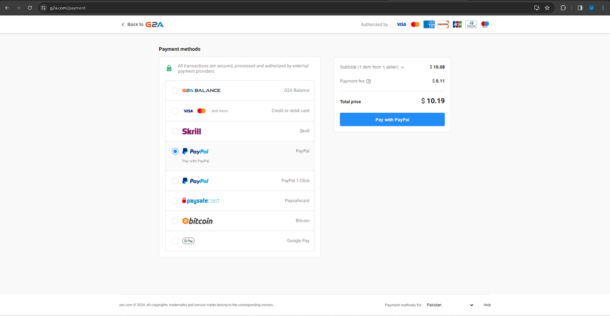
G2A.com has a price of 10.19 USD:
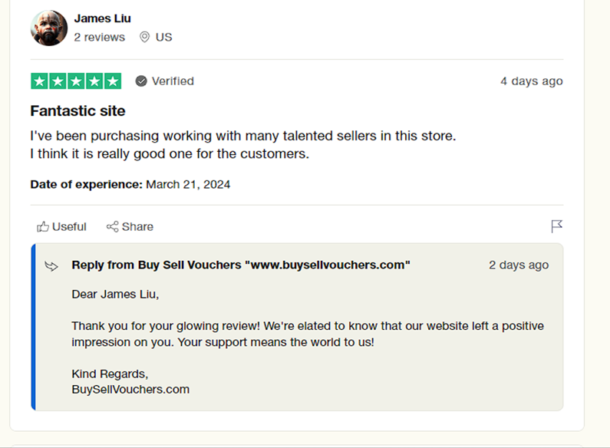
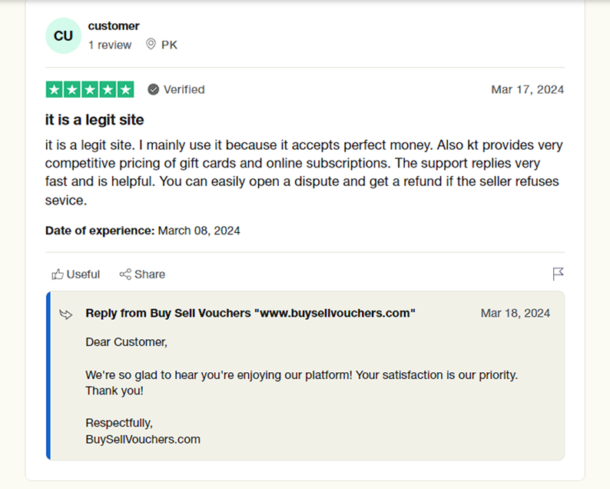
User reviews highlighting positive experiences with BuySellVouchers
If you’re concerned about the legitness of the BuySellVouchers platform, then you can look at the response of past customers of the platform to determine its legitness. A few reviews about the Buysellvouchers marketplace on Trustpilot.com are included below.
Insider Tips for Maximizing Savings
Tip #1: Timing is Key
If you want to obtain the best deals and discounts on BuySellVouchers, then timing is everything. Sellers may offer big discounts during special promotional events or during holidays. During these times, be sure to check prices regularly.
Tip #2: Explore Different Sellers
When you want to buy a gift card, be sure to explore different sellers and compare the prices among them. Your sentence is mostly correct, but it can be improved for clarity and consistency. Choose the seller that offers the lowest price and has a good reputation (high seller rating). You can evaluate a seller’s performance by looking at his reviews and successful sales history.
Tip #3: Take Advantage of Promotions
From time to time, there may be ongoing promotions on the BuySellVouchers or Razer platform. During these events, you can generally save even more money due to bigger discounts.
Tip #4: Bundle Deals
Some sellers on the platform also offer discounts for bulk purchases. These packages will save you more money than if you buy gift cards one by one. The bigger your order is, the more you can save. There are sellers who sell gift cards in bulk at very good prices.
Tip #5: Monitor Price Trends
Gift card prices can fluctuate from time to time. The product that you want to buy today may not be offered at the same price tomorrow. In such an event, your best option would be to wait for the price to go down again. To monitor the prices, you should be kept updated on the BuySellVouchers platform whenever you can.
Ensuring a Smooth Transaction
Account setup
To create an account on BuySellVouchers, click on the Register button at the top.
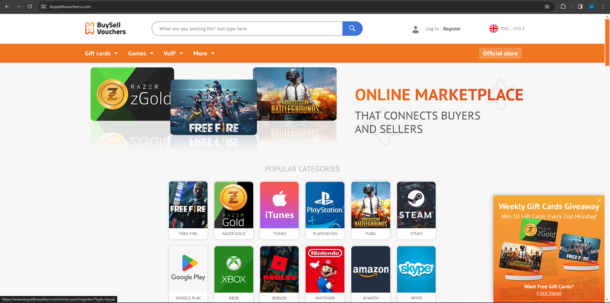
After that, you can either Sign Up using your existing Google gmail account or alternatively create your own unique BuySellVouchers account by entering a valid e-mail address, a username and password.
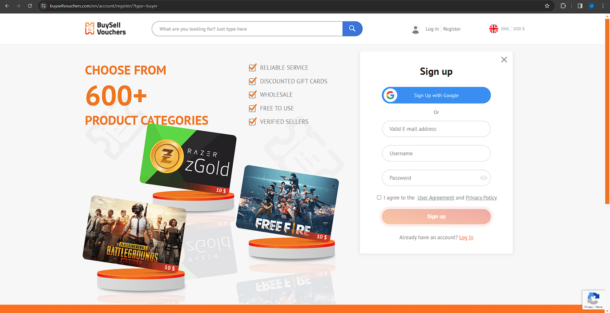
After you input your details and click on the Sign Up button, you will then be asked to verify your e-mail by clicking on the link you just received in your e-mail address. Do that and you’re all good to go.
A step-by-step guide to purchasing Razer Gold gift cards on BuySellVouchers
To browse all available Razer Gold gift cards on BuySellVouchers, you can either use the search function or browse the Razor Gold category.
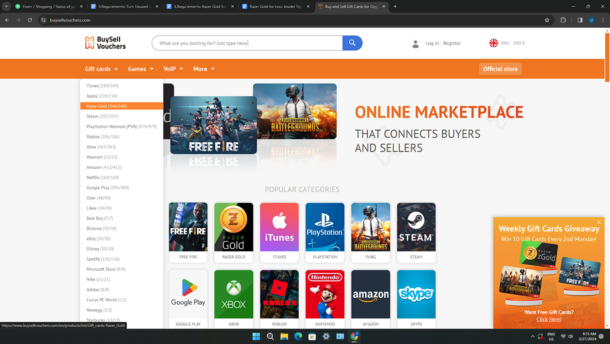
Choose the product that you want to buy and then after that, click on the Buy Now button. Select your desired payment method, enter your email address where you want to receive your product and then click on the Buy button.
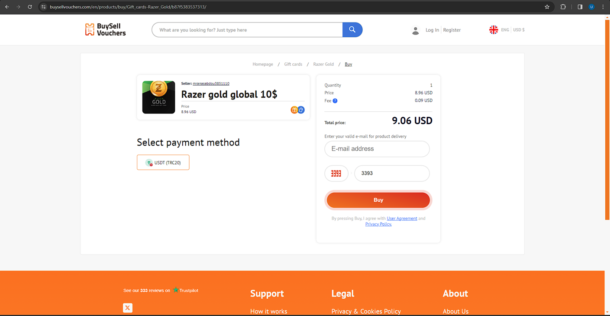
Wait for your order to be processed. After that, the gift card code will be delivered to you.
Tips for verifying the authenticity and value of gift card listings
To verify the authenticity and value of gift card listings, you can look at the seller’s reviews and feedback to determine if he’s a legit seller or not. If the reviews are generally positive, then you can go ahead and buy from him. If reviews are negative, you should tend to avoid him.Safety measures and precautions for buyers to avoid scams or fraud
To find the sellers with the most positive feedback, you can use the filter function on BuySellVouchers which will bring the sellers with the best feedback in descending order. Each seller has a seller level that determines their success with the platform. By buying from the top-rated sellers, there is nearly zero chance for you to get scammed. If you want 100% risk free purchases you can buy your gift cards from the Official BuySellVouchers Store where every product is offered by the official seller of the platform.Real-Life Success StoriesTestimonials from gamers who have purchased Razor Gold gift cards from BuySellVouchersBelow, you’ll find the feedback of a few people who have successfully purchased a $100 Razer Gold gift card from BuySellVouchers.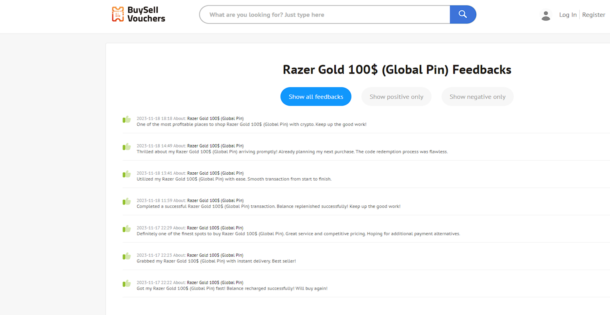
How buying and using discounted gift cards has helped people with financial concerns
Buying discounted Razer Gold gift cards allow people to purchase games that they weren’t able to previously due to financial issues. Using discounted Razer Gold gift cards allows you to buy games at a very cheap price and also get Razer Silver in return which you can redeem for even more rewards.
Addressing Common Concerns
Addressing skepticism or doubts about the legitimacy of discounted gift cards
Before anyone buys a discounted gift card for the first time, they have many doubts in mind. They wonder about the possibility of being scammed, but we can assure you that if you buy your discounted gift cards from BuySellVouchers Official Store, you will never face such a problem.
Clarifying buyer protection measures and recourse in case of issues
In case you face issues with your seller regarding your purchases, you can either contact him to discuss your issue and get it resolved. If the seller doesn’t reply or refuses to resolve your issue, you can contact the BuySellVouchers customer support. If you haven’t received your product, you might be able to get a refund as well.
Providing guidance on compliance with terms of use for Razer Gold gift cards
To prevent any future issues or misconceptions. Be sure to fully comply with the Razer Gold terms of service. Upon redeeming a Razor Gold gift card, the gift card balance will be added to your account and it must be used within one year. However, you are exempt from this if you live in certain areas where this is prevented by law.
Conclusion
Razer Gold gift cards allow you to top up your account and purchase games and in-game content in a fast and convenient way. If you look for cheap Razer Gold gift cards, then BuySellVouchers marketplace is the right place to go. So, if your budget is the main factor stopping you from buying gift cards, visit BuySellVouchers to get the most out of your budget.
Gaming News
The Esports Tech Revolution: Behind the Scenes of Canada’s Gaming CS:GO Championship Teams Phenomenon

This article delves into the unparalleled popularity of Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS:GO) and its successor, Counter-Strike 2 (CS2), in the Canadian esports scene. Highlighting the unique aspects that have endeared this franchise to millions, we explore the technological innovations, player dedication, and the vibrant community that have made Counter-Strike a standout series in the competitive gaming world.
The End of an Era and the Dawn of a New Chapter: The Transition From CS:GO to CS2
After 11 years of reign, Counter-Strike: Global Offensive was phased out to make room for Counter-Strike 2. This transition, executed by Valve, was not just a change of guards but a significant update intended to push players towards the newer iteration, CS2. Despite the mixed reactions from the community, this move illustrates Valve’s intention to keep the Counter-Strike franchise at the forefront of FPS esports.
Counter-Strike 2 introduces enhancements and adjustments, such as updated grenade mechanics and more intricate maps, though it has faced criticism for not retaining some of the beloved game modes and the perceived lack of precision found in CS:GO’s gameplay.
A Deep Dive Into CS2’s Core Mechanics: Understanding the Gameplay Enhancements
For many, Counter-Strike 2 appears to be a substantial update rather than a completely new installment. Leveraging the Source 2 engine, CS2 offers refined menus and gameplay mechanics, especially regarding grenade usage. At its core, the game remains a battle between terrorists and counter-terrorists, with success largely dependent on the player’s ability to aim and strategize.
The transition to CS2 has been designed to elevate the tried-and-tested Counter-Strike formula, avoiding radical changes that could alienate the franchise’s dedicated fanbase.
The Canadian Connection: Esports Popularity in Canada
In Canada, the Counter-Strike franchise has captivated a large audience, thanks to its intense gameplay, strategic depth, and the community that has built up around it. Canadian gamers and esports enthusiasts have been especially drawn to the series, fostering a competitive environment that has seen Canadian teams rise to prominence on the global stage.
This popularity is not just about the thrill of the game but also about the social and technological infrastructure that supports it, including high-speed internet access and gaming cafes that cater to the esports community.
The seamless integration of Ontario betting apps offer a wide variety of live betting options, has further enriched the viewing experience, allowing fans to become a part of the action in real-time.
Technology’s Role in CS:GO and CS2’s Success: Behind the Scenes of the Esports Phenomenon
The technological advancements in gaming hardware and software have been pivotal in the evolution of the Counter-Strike series from a gameplay and spectator perspective. High-refresh-rate monitors, specialized gaming peripherals, and the development of the Source 2 engine for CS2 have contributed to a more engaging and responsive gaming experience.
Additionally, streaming platforms like Twitch and YouTube have made it easier for fans to watch their favorite teams and players, significantly expanding the reach and popularity of Counter-Strike esports across Canada and beyond.
The Competitive Edge: Training and Precision in CS:GO and CS2
The precision and strategic depth of Counter-Strike gameplay require players to dedicate significant time to training and mastering the game’s mechanics. This aspect of the game has cultivated a highly competitive environment, where even minor improvements in skill can make a substantial difference in match outcomes.
The dedication of Canadian players to honing their skills has been a key factor in the success of Canadian teams in international competitions, highlighting the country’s commitment to excellence in esports.
Community and Culture: The Backbone of Counter-Strike’s Popularity
The vibrant community surrounding the Counter-Strike franchise is a testament to its enduring appeal. Forums, social media, and in-game communities have provided spaces for players to share strategies, celebrate victories, and commiserate over losses.
This sense of community has been instrumental in sustaining the game’s popularity over the years, creating a welcoming environment for newcomers and veterans alike. In Canada, this community aspect has been particularly strong, with local tournaments and online leagues fostering a sense of belonging and camaraderie among players.
The Future of Counter-Strike in Canada: What Lies Ahead for Canadian Esports
As Counter-Strike continues to evolve with the introduction of CS2, the Canadian esports scene is poised for further growth. The combination of technological innovation, a dedicated player base, and supportive community infrastructure suggests a bright future for Counter-Strike esports in Canada.
As Valve continues to update and refine CS2, addressing the community’s feedback, it’s expected that the game will mature, attracting even more players and spectators. The ongoing development of esports facilities, along with the increasing recognition of esports as a legitimate competitive field, will likely lead to more Canadian talent rising to international prominence.
Player Development and Talent Nurturing: Cultivating the Next Generation of CS Stars

The nurturing of esports talent in Canada is a critical factor in the sustained popularity and success of the Counter-Strike franchise. Through grassroots initiatives, gaming camps, and educational programs focusing on strategic game play and teamwork, young players are being groomed to become the next esports stars.
This focus on talent development is crucial for maintaining Canada’s competitive edge on the global stage and ensures that the Counter-Strike community remains vibrant and dynamic.
The Role of Sponsorships and Partnerships: Fueling the Growth of the Esports Ecosystem
Sponsorships and partnerships with brands and tech companies have played a significant role in the expansion of the Counter-Strike esports scene in Canada. These collaborations provide essential funding for tournaments, team sponsorships, and event hosting, creating opportunities for players to showcase their skills on larger platforms.
The support from these partnerships not only bolsters the professional scene but also helps in the development of community-based events, making esports more accessible to a broader audience.
The Evolution of Esports Venues: The Importance of Physical Spaces in the Digital Realm
The establishment of dedicated esports venues in Canada, such as gaming arenas and cafes, has been instrumental in bringing the community together for live events. These spaces offer fans the chance to experience the thrill of live competition and interact with fellow enthusiasts, further solidifying the social bonds within the Counter-Strike community.
As the popularity of CS:GO and CS2 continues to grow, these physical venues play a pivotal role in the ecosystem, serving as hubs for both casual and competitive play.
The Impact of Streaming and Content Creation: Expanding the Reach of Counter-Strike Esports
Streaming platforms and content creation have significantly contributed to the popularity of Counter-Strike in Canada. By providing a means for players to broadcast their gameplay, share tips, and entertain fans, these platforms have made esports more accessible to a wider audience.
The personalities and narratives that emerge from the streaming world add depth to the competitive scene, creating a rich tapestry of stories that engage fans beyond the game itself.
The Global Stage: Canada’s Presence in International Competitions
Canadian teams and players have made their mark on the international Counter-Strike scene, competing in and winning prestigious tournaments. This global presence not only showcases the talent within the Canadian esports community but also brings international attention to Canada as a competitive gaming powerhouse.
The successes of these teams on the world stage inspire the next generation of players and contribute to the country’s reputation in the global esports arena.
The Educational Aspect: Learning Beyond the Game
Counter-Strike and its esports scene offer more than just entertainment; they provide educational opportunities that extend beyond the game. Skills such as teamwork, strategic thinking, and quick decision-making are integral to success in Counter-Strike and are highly transferable to real-world situations.
The strategic depth of the game encourages players to analyze and adapt, fostering a mindset that values planning and execution. In Canada, the educational potential of esports is beginning to be recognized, with programs and initiatives aimed at leveraging gaming for learning and development.
A Flourishing Future: The Enduring Legacy of Counter-Strike in Canada
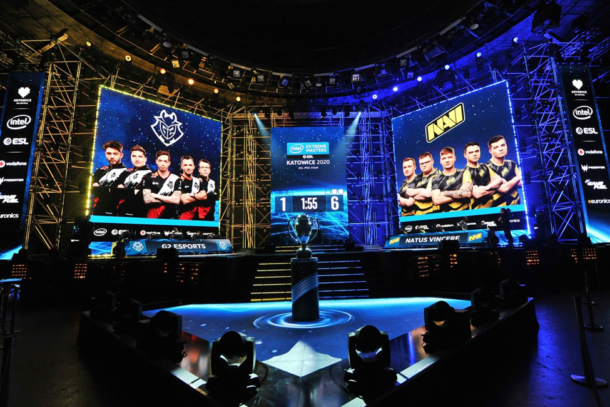

As we look to the future, the Counter-Strike franchise’s impact on the Canadian esports landscape is undeniable. From fostering a dedicated community to contributing to the growth of a robust esports ecosystem, Counter-Strike has played a pivotal role in shaping the competitive gaming culture in Canada.
With ongoing support from developers, sponsors, and the community, the legacy of Counter-Strike is set to continue, promising a vibrant and exciting future for Canadian esports.
-

 Guides4 years ago
Guides4 years ago6 Proven Ways to Get more Instagram Likes on your Business Account
-

 Mainstream9 years ago
Mainstream9 years agoBioWare: Mass Effect 4 to Benefit From Dropping Last-Gen, Will Not Share Template With Dragon Age: Inquisition
-

 Guides2 months ago
Guides2 months agoExplore 15 Most Popular Poki Games
-

 Guides1 year ago
Guides1 year agoGan Rubik’s Cube vs. Traditional Rubik’s Cube: Key Differences and Advantages
-
Mainstream14 years ago
How to Fix Modern Warfare 2 Problems/Freezings
-

 Mainstream11 years ago
Mainstream11 years agoNew Assets Found for Half Life Episode 4
-
Guides15 years ago
GTI Club+: Rally Cote d’Azur – PS3 Cheats
-

 Casual5 months ago
Casual5 months ago8 Ways to Fix Over-Extrusion and Under-Extrusion in 3D Printing
